Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-05 Origin: Site





NFPA 110 Standards have strict rules for emergency power systems. You need to follow these rules to keep people safe. They also help you follow the law. These rules help your business keep working when the power goes out. Many places do not follow the rules because they skip maintenance. Some do not have enough data to show their systems work well. New generator solutions, like LIYU's gas-fired internal combustion generator sets, give steady and strong power. These systems help you follow the rules and keep everyone safe.
NFPA 110 Standards help keep emergency power systems safe. These rules make sure people and equipment stay safe in power outages.
It is very important to test generators often. Test your system every month. Do a big test once a year. This makes sure it will work when you need it.
You need to know the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 systems. Level 1 systems are needed for safety. Level 2 systems help protect equipment and data.
Following NFPA 110 is not just about being safe. It also helps you avoid legal trouble. Local officials check these rules. If you do not follow them, you can get fines or lose permits.
Check your building to find the right generator class and type. This helps your building get ready for emergencies.

It is important to know why NFPA 110 Standards are needed. These standards give clear rules for emergency and backup power systems. They help you make sure your building has backup power if the main power stops. This keeps people safe and protects equipment.
The main goals of NFPA 110 Standards are:
Give rules for how emergency and backup power systems should work.
Make sure you have another way to get power when the lights go out.
If you follow these standards, you help stop dangerous problems. You also help your building keep working during emergencies.
NFPA 110 Standards talk about many parts of emergency power systems. You need to think about planning, design, putting in the system, using it, testing, starting it up, and keeping it working. Every step is important to follow the rules.
The standards talk about different system levels. Here is a table to help you see what they mean:
System Level | Description |
|---|---|
Level 1 | Systems where not working could cause people to get hurt or worse, like fire alarms and emergency lights. |
Level 2 | Systems that are not as risky for people but could still be dangerous if they stop, like heating, cooling, or elevators. |
You should also know that the newest NFPA 110 Standards have some updates. For example, there are new rules for fuel cell systems to match other codes. The standards also explain better how to design and test energy converters for different problems. These changes help you keep up with new technology and safety needs.
You must follow NFPA 110 Standards if you run certain places. These include:
Data centers
Research labs
Response centers
If your building needs emergency power to keep people or data safe, you must follow the rules. Many checks look at things like exhaust, where equipment is, fire safety, planning for problems, building, controls, starting, testing, how well it works, and on-site needs. You should check these things often to make sure your system follows the rules.
By knowing the purpose, scope, and who must follow the rules, you can get your building ready for emergencies. You also help keep people safe and follow the law.
Following NFPA 110 Standards helps save lives. These rules make sure your emergency power systems are always ready. If you do not follow the rules, you face big problems:
You might fail inspections and have to stop work.
You could get fined or your safety systems might not work in a blackout.
Hospitals need working generators. If they stop, patients needing machines or surgery could be in danger.
Studies show that following the rules often can stop most failures in emergencies. Good systems break less than 1% of the time. You should test your system every month and do a big test once a year. This helps make sure it works when you need it.
You also need to think about the law. Local officials make sure you follow NFPA 110 Standards. If you do not, you could get fined, lose your permit, or even get in legal trouble.
The NFPA makes the rules but does not check if you follow them. Local officials, like building code offices, do the checking. They can use fines, take away permits, or even start a criminal case if you break the rules.
The Joint Commission and CMS also want you to follow the rules. If you do not, you could lose your license or money.
Following NFPA 110 Standards keeps your business open. These rules help you get ready for emergencies and keep important systems working. The table below shows how following the rules helps your business:
Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Compliance Requirement | NFPA 110 says you must install, use, and take care of emergency and backup power systems. |
Impact on Operations | Makes sure hospitals can keep helping people when the power goes out. |
Emergency Preparedness | Helps places get ready for emergencies and keep people safe. |
You might have problems like not enough money, not enough trained workers, or trouble keeping up with tests. You can fix these by doing the most important jobs first, teaching your team, or hiring experts. Reminders can also help you remember to do tests.
It is important to know the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 emergency power supply systems (EPSS). Level 1 systems keep people safe from harm. If these systems stop working, someone could get hurt or even die. Level 2 systems help protect things like equipment or data. If Level 2 systems fail, people are not in danger, but you might lose important items.
Classification | Description |
|---|---|
Level 1 EPSS | Gives power where losing it could cause death or serious injury. |
Level 2 EPSS | Supports things that are not as important for keeping people safe. |
Places that need Level 1 systems are:
Hospitals
Emergency rooms
Critical care centers
Level 2 systems are good for:
Manufacturing plants
Telecommunications centers
Offices where losing power hurts business, not safety
Level 1 systems have tougher rules for testing and maintenance than Level 2 systems.
NFPA 110 Standards have class rules based on how long a generator can run without more fuel. The class you pick depends on what your building needs.
Class | Minimum Runtime |
|---|---|
Class 0.083 | 5 minutes |
Class 0.25 | 15 minutes |
Class 2 | 2 hours |
Class 6 | 6 hours |
Class 48 | 48 hours |
Class X | 96 hours |
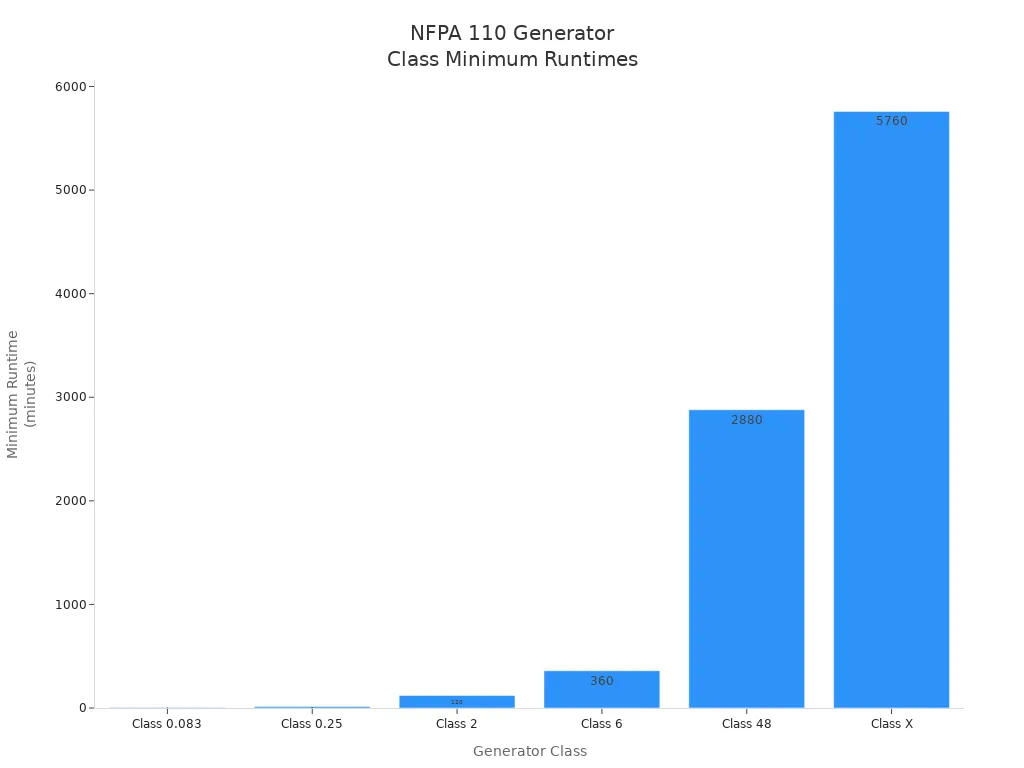
Some places, like hospitals, may need Class X generators that last 96 hours. Other places may only need a generator that runs for a short time.
You should check your building to see which system and class you need. Start by asking questions like:
What things must keep working if the power goes out?
How long do you need backup power to last?
What could go wrong if you lose power?
A good check helps you find weak spots and get ready for emergencies. You can use a gap analysis to see if your system meets NFPA 110 Standards. This helps you make a plan to fix problems and keep everyone safe.
NFPA 110 Standards use three main ways to sort generator systems:
Classification Level | Description |
|---|---|
Level 1 | Most strict; failure could cause death or serious injury. |
Level 2 | Less strict; failure does not put lives at risk. |
Class | Tells how long the generator can run without more fuel. |
Type | Tells how fast the generator starts after losing power. |
You must pick the right generator type for your building. For example, a Type 10 system gives power back in 10 seconds, which is very important for hospitals.
NFPA 110 Standards help keep emergency power systems working well. You need to test your generators a lot and write down what you do. Using new tools like LIYU's gas-fired generator sets helps you follow the rules. Checking your system often helps you spot problems early and get ready for new rules.
Maintenance Activity | Frequency |
|---|---|
Weekly exercising of generators | Weekly |
Monthly inspections of fuel systems | Monthly |
Annual load bank testing | Annually |
Watching your system all the time keeps it current.
Regular checks help you find problems and make things safer.
NFPA 110 helps you keep emergency power systems safe and reliable. You use these rules to make sure backup generators work during power outages. This protects people and equipment.
You should test your generator every month. You also need to do a big test once a year. Regular testing helps you find problems early and keeps your system ready.
Yes, LIYU gas-fired internal combustion generator sets help you meet NFPA 110 standards. These generators provide reliable power, support regular testing, and offer features that help you stay compliant.
Local officials, like fire marshals or building inspectors, check your compliance. They look at your records and inspect your equipment. You must keep good records to show you follow the rules.