




A genset is also called a generator set. It is a machine that has an engine and a generator. It makes electricity when grid power is not there or is not steady. Many industries use gensets for backup power. This is important in places with many outages and more buildings being built. More people need generator sets in Asia Pacific and Africa. This is because cities are growing, grids are weak, and governments want to be ready for emergencies.
A genset is a full power machine. It has an engine and a generator. It can work by itself to give electricity. It helps when the main power goes out.
Gensets have many parts. These include the engine, alternator, fuel system, and control panel. All these parts work together. They help give steady and safe power.
Diesel gensets are strong and last a long time. They are good for heavy use. Gasoline gensets are lighter. They are better for small jobs or homes.
Gensets give backup power you can trust. They help hospitals, businesses, and faraway places. They keep important things working during power outages.
Picking the right genset means knowing your power needs. You should know what fuel type you want. You also need to choose between a portable or stationary model. This helps you get the best results.
A genset is short for generator set. It is a machine that makes electricity by itself. It has an engine and a generator in one unit. This means it can work alone if the grid stops working. ISO 8528 and other rules say a genset must be safe and reliable. These rules make sure a genset gives power when people need it. Gensets help homes, businesses, and emergency workers.
Note: The phrase "what is a genset" means a full power system, not just one part.
A generator set has more than just an engine and generator. It has many systems to help it run well and safely. Here are the main parts you find in most gensets:
Engine: Makes mechanical energy.
Alternator: Changes mechanical energy to electrical power.
Fuel system: Holds and sends fuel.
Cooling system: Stops the engine from getting too hot.
Lubrication system: Lowers rubbing inside the engine.
Exhaust system: Moves out gases and cuts noise.
Battery: Starts the engine and powers controls.
Control panel: Lets people check and use the genset.
All these parts work together to give steady electricity. A genset is different from a simple generator because it has everything built in. A regular generator only makes electricity from mechanical energy. It needs another engine or power source to work. But a genset can start and run by itself.
Feature | Generator | Genset |
|---|---|---|
Main Function | Converts mechanical energy into electricity | Provides a complete power solution |
Engine Included? | No | Yes |
Fuel System? | No | Yes |
Control Panel? | No | Yes |
Usability | Needs external power source | Works independently |
A genset is easy to use for backup or far-away power. It is good for places where grid power is weak or missing. Many homes and businesses use gensets for steady electricity.
If you want power you can trust, look at LIYU Group's containerized generator sets. These products give strong and steady power for homes and businesses. Check out LIYU Group's options to find the best genset for you.
A genset has many important parts that help make power. These parts work together to keep the system safe. The main components are the engine, alternator, control panel, and base frame. Each part does something special.
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Engine | Uses fuel to make mechanical energy. It runs for a long time at steady speeds. |
Alternator (Generator Head) | Changes mechanical energy into electrical energy. It can handle heavy use. |
Control Panel | Shows how the system is working. Lets people start, stop, and check the genset. |
Base Frame (Chassis) | Holds all the parts together. Keeps the genset safe and steady. |
Other parts of a genset are the fuel system, cooling system, exhaust system, and battery. The fuel system keeps and sends fuel to the engine. The cooling system stops the engine from getting too hot. The exhaust system takes away gases. The battery helps start the engine. These parts help the genset work well in many places.
Tip: Always look at the control panel and fuel system before you start the genset. This helps stop problems and keeps things safe.
How does a genset work? First, the engine burns fuel like diesel or gasoline. The engine makes mechanical energy. The alternator turns this energy into electrical power. This uses electromagnetic induction. The control panel helps people manage and watch the system. The base frame holds all the parts together.
Here is an easy way to see how do generators work in a genset:
The engine burns fuel and makes mechanical energy.
The alternator takes this energy and makes electricity.
The control panel shows how the system works and lets people control it.
The base frame keeps everything together.
How do generators work in other systems? Some use wind, solar, or water to make power. A genset uses fuel and an engine. This makes it good for backup or portable power.
Efficiency is important for every genset. The table below shows how different types work:
Genset Type | Typical Efficiency Range (%) | Notes on Efficiency Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Diesel Generators | 30 - 45 | Work best at 70-80% of full load |
Gasoline Generators | 20 - 35 | Not as efficient; inverter types can reach 35-40% |
Natural Gas Generators | Lower than diesel | Combined heat and power can reach 80-90% total |
A genset gives steady power when the grid does not work. It is good for homes, businesses, and far-away places. If you want power you can trust, LIYU Group has gas generators and containerized gensets. These products give strong, safe, and steady power for many needs.
A diesel genset makes electricity with a diesel engine. It is the most common type in the world. Many industries and building sites use it for strong power. Diesel gensets save fuel and last a long time. They work well in tough places and need less fixing than other types. Companies pick diesel gensets because they are tough and work well.
Diesel gensets sell the most worldwide. They are popular because they are easy to fix and last longer. Factories like them since they can run for many hours.
Here is a table with the main good and bad points:
Feature | Diesel Genset Advantages | Diesel Genset Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Fuel Efficiency | Uses less fuel, saves money over time | Costs more at first |
Durability | Made for hard jobs, lasts longer | Makes more noise and shakes |
Portability | N/A | Big and heavy |
Safety | Fuel is safer to keep | Must stay dry or it can rust |
Environmental | N/A | Makes more pollution |
A gasoline genset uses a gasoline engine to make power. It is best for homes and small shops. People like gasoline gensets because they are light and easy to start. They cost less to buy and are good for short or small jobs. About 40% of gasoline gensets are used in homes. Small stores and service shops use them for backup power.
Application Segment | Market Share (2024) | Key Drivers and Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Residential | ~40% | Cheap, easy to move, simple to set up |
Commercial | Big part | Small, starts fast, good for short use |
Gasoline gensets are quieter than diesel gensets. They are easier to carry and store. But they do not last as long and need more repairs.
Gensets can be portable or stationary. Portable gensets are good for outdoor parties, camping, and home emergencies. They are easy to move and use. Most portable gensets have gasoline engines. Stationary gensets are for big homes, companies, and factories. They give more power and can run for a long time. Diesel gensets often power stationary models.
Characteristic | Portable Generators | Stationary Generators |
|---|---|---|
Power Output | 1kVA to 10kVA | 10kVA to thousands of kVA |
Installation | Easy to set up, can move | Needs experts, has strong covers |
Use Cases | Outdoor fun, camping, home backup | Big homes, companies, factories |
Operation | Uses petrol, starts by hand | Uses diesel or petrol, starts by itself |
Advantages | Easy to move, cheap, flexible | Always ready, starts on its own, lots of power |
Maintenance | Needs more fixing | Needs less fixing because it is automatic |
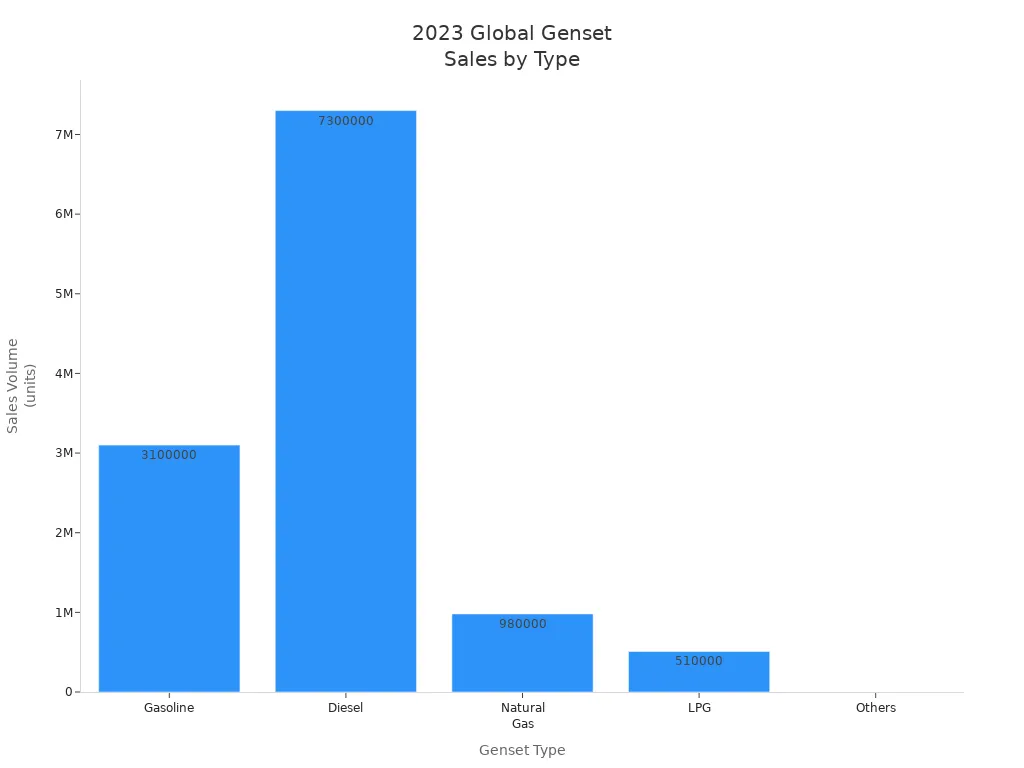
Natural gas gensets are becoming more popular. Hospitals and computer centers use natural gas gensets for cleaner and quieter power. These gensets make less pollution and can run longer. More natural gas gensets are being used in North America and Western Europe every year.
Many people use gensets for reliable power. Hospitals and data centers need them during outages. Water treatment plants also depend on gensets to keep working. Diesel generators start fast, often in under 10 seconds. They can run for many hours if needed. Automatic transfer switches spot grid failures right away. These switches turn on the genset without waiting. This helps protect public health and stops money loss. Gensets help the grid by handling peak loads. They also work with microgrids to keep power steady. Regular maintenance like oil changes and battery checks is important. This keeps the genset ready for emergencies.
Tip: Routine checks and expert service help stop downtime. They also make the equipment last longer.
Gensets are useful in many places. Construction sites, hospitals, and farms all use them. Emergency services need gensets for backup power in disasters. They power big machines like cranes and welders. Gensets work well in far-away areas with weak or no grid power. Many models are portable and containerized. This makes moving them easy by land, sea, or air.
Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
Portability | Easy to move to remote places for mining or farming. Good for rescue work too. |
Scalability | Units can join together for small or big jobs. |
Adaptability | Can use automatic or manual controls. Works locally or from far away. |
Emergency Preparedness | Quick setup keeps important services running in crises. |
Gensets save money for backup power. Standby generators cost $7,000 to $15,000 at first. This is less than solar panels with batteries. Portable generators cost even less. But you must pay for fuel and fixing over time. Yearly maintenance costs $200 to $600. Over 20 years, gensets can cost more than solar systems. But gensets give instant power and are flexible. Fuel-saving models use less diesel and cut emissions. EPA Tier 4 rules lower pollution by about 90% compared to old models.
Backup Power Option | Initial Investment Cost Range |
|---|---|
Portable Generators | $1,400 – $4,500 |
Standby Generators | $7,000 – $15,000 |
Solar Panel + Battery | $25,000 – $30,000 |
Many businesses need backup power to keep working. Data centers use backup generators so servers do not stop. Hospitals need backup power to keep machines running. Farms and emergency teams use backup power for safety and work. Shipping companies use backup generators for reefer containers. These keep food and medicine safe while moving.
Application Area | Description | Industrial/Commercial Contexts |
|---|---|---|
Data Centers | Keeps servers on all the time | IT, Technology, Hosting Services |
Healthcare Facilities | Backup power for important machines | Hospitals, Medical Centers |
Emergency Operations | Helps important services during blackouts | Emergency services, Agriculture |
Remote Locations | Gives power where there is no grid | Military, Disaster Response, Industry |
Reefer Containers | Keeps cold cargo safe with backup power | Shipping, Logistics, Cold Chain |
Tip: Backup power helps businesses stop losses and keeps people safe.
Backup power keeps important places safe when power goes out. Natural gas backup generators give steady power and turn on fast. They cost less to use and fix than diesel ones. Smart control systems help backup power work well with the grid. Hospitals and data centers use backup power to protect lives and data. These systems turn on by themselves and keep things running.
Backup power keeps medical tools and emergency systems working.
It protects data and helps businesses keep going.
Using backup power helps places follow rules and avoid fines.
Gensets and UPS systems work together for backup power. UPS gives quick power for a short time. Backup generators give power for hours or days. This setup keeps hospitals and data centers safe.
Remote power jobs have many problems. Getting fuel in deserts is hard and slow. Hot weather and dust can break backup generators. This means more repairs. Diesel backup power uses more fuel and breaks faster in tough places. Workers must travel far to fix things, which costs more and takes time.
Hybrid solar-battery systems with backup generators work better and use less fuel. Solar panels in deserts need cleaning and strong frames to last. Good panels and smart plans help keep power on in hard places. Extra systems help remote power keep working if one part stops.
Note: In remote places, hybrid systems give better power and cost less.
Picking the best power solution means knowing how generator sets work. You should know what they do and why they help. Make a list of all your devices. Add up the total wattage you need. Choose a generator set that matches your needs. Look at the fuel type, noise level, and if you can move it. Groups save money and get steady power by picking the right unit. They should think about where they use it now and later. Remote monitoring and automatic switches make things easier.
A generator only makes electricity from mechanical energy. A genset has an engine, generator, and other systems in one unit. It can work alone and provide power when the grid fails.
Most gensets can run for 8 to 24 hours on a full tank. Some large models run longer if they have enough fuel. Always check the manual for safe running times.
People use gensets in hospitals, factories, farms, and homes. They also use them for backup power and in remote places. Genset in shipping helps keep goods safe during transport.
A genset container holds the genset and protects it from weather and damage. It makes moving and setting up the genset easier. Many companies use genset containers for big projects.
List all devices you want to power. Add up their wattage. Pick a genset that gives more power than your total need. This helps the genset work safely and last longer.