Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-18 Origin: Site





A commercial generator gives your business power when the electricity goes out. You need it to keep lights, computers, and equipment working during outages. Commercial generators come in different sizes. Their power starts at 50 kW and can go over 3 megawatts. You can guess the size you need by using 10 watts for each square foot. This equipment helps stop expensive downtime and keeps your business safe.
A commercial generator gives backup power to your business during outages. It protects your equipment and stops expensive downtime.
Pick the right size generator by listing your power needs. Add extra capacity for surges and to keep systems safe.
Commercial generators use fuels like diesel or natural gas. They come in types like standby, portable, and inverter for different business needs.
Always put generators outside with good airflow. Use automatic transfer switches and follow safety rules to keep people and property safe.
Regular maintenance and the right fuel help your generator work well and last longer. This makes sure you have power when you need it most.

A commercial generator gives your business power when the lights go out. It is bigger and stronger than a home generator. You use it for offices, stores, schools, and hospitals if the main power stops. It runs on natural gas or diesel fuel. The engine and cooling parts are made for hard work. It gives more power, so your business keeps working. It is different from small units because it can help big spaces and important systems. You count on a commercial generator for steady backup power and to keep your business going.
You should know what makes a commercial generator special. Here are the main things:
Feature | Commercial Generators | Industrial Generators |
|---|---|---|
Power Output | Usually 10 kW to 100 kW, good for small businesses | Goes from 20 kW to over 3 MW, for big operations |
Size and Design | Smaller, fits in tight spaces | Bigger, made for large buildings |
Fuel Types | Uses natural gas, propane, diesel, gasoline, or both | Mostly diesel, sometimes gas |
Operational Features | Easier controls, simple to use | Has extras like automatic switches, remote checks |
Cost | Cheaper to buy and fix | Costs more to buy and maintain |
Durability & Maintenance | Not as tough, needs less fixing | Tougher, needs more repairs |
Noise & Environmental Impact | Quieter, meets normal rules | Louder, must follow strict rules |
Typical Applications | Used in stores, offices, small businesses | Used in factories, power plants, big places |
Commercial generators come in many sizes. They start at 20 kW and go up to over 3,000 kW. Common sizes are 75 kW, 100 kW, and 250 kW. You choose the size that fits your business. Medium sizes work well for schools, hospitals, and food services.
Big brands make most commercial generators. You see names like Briggs & Stratton, Caterpillar, Cummins, Generac, and Kohler. These companies give you backup power you can trust. They make generators for all kinds of businesses.
You need to think about the price of a commercial generator. Prices go from $300 to $450 for each kW. For example, a 70 kW generator might cost $17,900. A 350 kW one can cost $64,900. It costs $10,000 to $20,000 more to install, depending on size and setup. The total price depends on how much power you need, the brand, and how hard it is to install.
A commercial generator stops you from losing money when the power goes out. It connects to your main power system. When the power fails, it turns on in seconds. An automatic switch moves your business to generator power. Your lights, computers, and machines keep working. This backup power keeps your money safe and your business strong. You do not lose data and your customers stay happy. Power outages cost businesses a lot of money every year. A generator helps your business stay safe and keep working.
Tip: Pick a generator that fits your business and important systems. Good backup power keeps your business running in an emergency.
A commercial generator has many parts. Each part does something important. You should know these parts to see how the generator works. Here is a table that lists the main components and what each one does:
Component | Function |
|---|---|
Engine | Gives mechanical energy to power the generator. |
Alternator | Changes mechanical energy into electrical energy. |
Fuel System | Stores and moves fuel to the engine using tanks, lines, pumps, and filters. |
Voltage Regulator | Keeps the voltage steady to protect your equipment. |
Cooling System | Stops the engine from getting too hot by moving coolant and air. |
Exhaust System | Removes gases from the engine and lowers noise. |
Lubrication System | Sends oil to engine parts to cut down friction and heat. |
Battery & Charger | Starts the engine and keeps the battery ready. |
Control Panel | Lets you start, stop, and check the generator's status. |
Starter Motor | Uses battery power to turn on the engine. |
Governing System | Controls engine speed for steady power. |
Frame/Chassis | Holds all the parts together and gives support. |
Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) | Switches power from the grid to the generator during an outage. (Often installed nearby) |
Note: The automatic transfer switch is not inside the generator. It is very important for safe and quick power changes.
You can learn how a generator makes electricity by following these steps:
Fuel Storage and Delivery: The fuel system keeps fuel in a tank. It sends fuel through pipes and pumps to the engine. Filters clean the fuel before it gets to the engine.
Combustion: The engine mixes fuel and air. It burns the fuel inside cylinders. This makes hot gases that push the pistons.
Mechanical Energy Creation: The pistons move up and down. They turn the crankshaft. This changes the energy from burning fuel into spinning motion.
Alternator Activation: The crankshaft spins the rotor inside the alternator. The rotor moves inside the stator and makes an electric current.
Voltage Regulation: The voltage regulator checks the output. It changes the current to keep the voltage steady and safe for your devices.
Cooling and Exhaust: The cooling system moves coolant and air to keep the engine cool. The exhaust system takes away gases and lowers noise.
Power Distribution: The generator sends electricity to your building. The automatic transfer switch moves your power source from the grid to the generator when needed.
Tip: Take care of the fuel system, filters, and oil. This helps your generator work well and stops breakdowns.
You need to follow safety rules when you use a generator. These steps help keep people and your business safe:
Put the generator outside or in a room with good airflow. This stops carbon monoxide from building up.
Keep the generator on a flat, strong surface. Make sure it is above flood levels.
Use carbon monoxide detectors near the generator and inside your building.
Install an automatic transfer switch. This stops power from going back to the grid and keeps workers safe.
Store fuel in safe, approved containers. Keep it away from the generator and heat.
Never refuel the generator while it is running. Let it cool down first.
Use locks and barriers to stop theft or tampering.
Hire a licensed electrician to install the generator and transfer switch.
Check the generator often for leaks, strange sounds, or blocked vents.
Keep at least 3 to 4 feet of space around the generator. Put it at least 15 feet from doors, windows, or vents.
Use GFCI outlets and grounded cords to stop electric shocks.
Follow all local codes and NFPA rules for installation and use.
Teach your staff how to shut down the generator in an emergency and follow safety steps.
Safety Alert: Carbon monoxide is very dangerous. Always use your generator in a place with good airflow and put CO alarms nearby.
You might wonder how commercial and residential generators are not the same. The biggest differences are in power, strength, fuel, and what they do. Check the table below to compare them:
Generator Type | Power Output Range (kW) | Typical Usage Description |
|---|---|---|
Residential | 5 - 50 | Powers home appliances like refrigerators, lights, and HVAC systems |
Commercial | 25 - several hundred | Runs entire buildings, offices, stores, and industrial equipment |
A commercial generator gives a lot more power than a home one. It can run big things and work for many hours. It is made with strong parts and lasts a long time. Most commercial generators use diesel or natural gas. These fuels are good for long use and big jobs. Home generators often use propane, gasoline, or natural gas. They are smaller, quieter, and simple to put in.
Here are some other ways they are different:
Commercial generators need experts to install and check them. They are bigger and make more noise.
Residential generators are easier to put in. You can often take care of them yourself.
Commercial ones help important business systems. They keep your business safe if the power goes out.
Residential ones keep your house comfy by running basic things.
Pick a generator that fits what you need. Use a residential generator if you want your house to work during storms or short blackouts. It keeps your fridge, lights, and heat or air on.
Choose a commercial generator if you have a business, school, or hospital. It gives backup power to all your systems. You will not lose money or data if the power stops. It keeps your workers and customers safe.
Tip: Businesses should get a commercial generator for important work. It turns on by itself, keeps your systems working, and protects your money.
A commercial generator is best for places where losing power costs money or puts people in danger. It keeps your business open, protects your machines, and follows safety rules.
You can pick from different commercial generators. Each type works best for certain jobs. Here is what you should know:
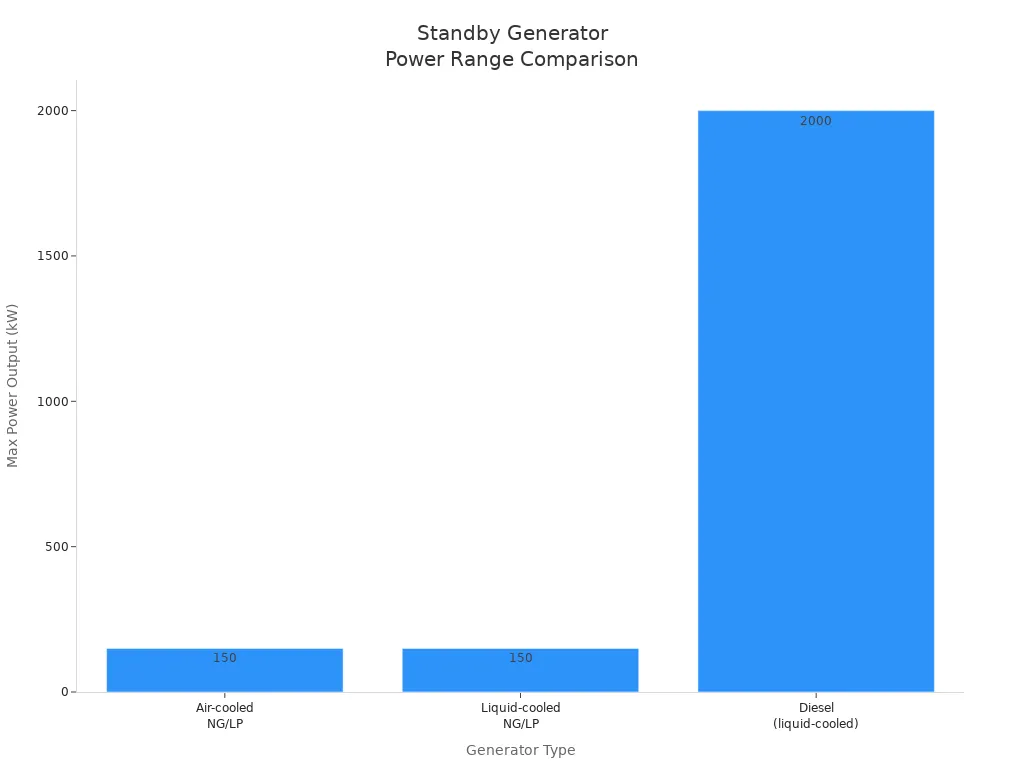
A standby generator gives backup power by itself. It connects to your building's power system. When the power stops, it starts in a few seconds. This type is best for businesses that need steady backup power.
Generator Type | Power Range (kW) | Fuel Options | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Air-cooled NG/LP | Up to 150 | Natural Gas, Propane | Good for short outages, cost-effective |
Liquid-cooled NG/LP | Up to 150 | Natural Gas, Propane | Handles higher loads, longer operation |
Diesel (liquid-cooled) | 20 - 2000+ | Diesel | Used in hospitals, data centers, long outages |
Diesel generators are used for big standby jobs. They last a long time and work well in important places. Natural gas units connect to gas pipes, so you do not need to keep fuel on site. Propane is good for country areas.
Tip: Standby generators cost more but help you worry less. They keep your business safe from losing money.
Portable generators are simple to move around. You can use them for short power needs at work sites, events, or repairs. They use gasoline, diesel, or propane.
Pros:
Cheaper than permanent generators
Easy to move and use
Good for short-term power
Cons:
Not as strong as standby units
You must start and refuel them yourself
Loud and must stay outside
Many businesses rent portable generators for quick jobs or emergencies. Rental companies let you rent by the day, week, or month. You do not have to fix or take care of them.
Inverter generators use new technology. They change engine speed to match your power needs. This saves fuel and makes less noise. Inverter units make clean power, so they are safe for computers and special tools.
Save fuel and are quiet
Give steady power for electronics
Easy to move and take care of
You can use inverter generators in offices, events, or places where quiet is important. They are good for sensitive equipment.
Note: You can rent any type of generator. Renting gives you choices and expert help for short-term needs.
You must pick the right size generator for your business. First, make a list of everything you want to power. Write down all the equipment and systems. Check how much power each one uses when it starts and when it runs. Motors use more power when they start up. Use a clamp-on ammeter to see how much power you use during busy times. Change the amps you find into kilowatts to be sure. Add up the kilowatts for things you need in an emergency. Always add extra power, about 25%, for sudden surges. For stores, use 10 watts for each square foot and add 50 kW. Other buildings use 5 watts for each square foot.
Application Type | Base Kilowatt Value | Watts per Square Foot | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Retail | 50 kW | 10 W/sq ft | Grocery stores, restaurants, convenience stores |
Other Commercial | 50 kW | 5 W/sq ft | Offices, schools, clinics |
Getting the right size stops overloads and saves money. It also keeps your business running. Always follow the National Electrical Code to stay safe.
Tip: Add 25% more power to your total for best results.
You can pick from a few fuel types for your generator. Diesel and natural gas are the most used. Diesel generators last a long time and work well. They are about 40% efficient. Natural gas generators are cleaner and connect to pipelines. You do not have to store fuel for them. But they need more care and may stop if the gas line fails. Propane lasts a long time but is not as efficient as diesel. Gasoline is mostly for small portable generators. It is not good for big businesses.
Diesel generators cost more to run but last longer. Natural gas units are cheaper to fuel and can run for a long time. Dual-fuel systems use both diesel and natural gas. This gives you more choices. The price of fuel and how much care you need changes your costs over time.
You need to put your generator in a good spot. Keep it at least 20 feet away from buildings. Do not put it near busy places. Use walls or fences to block sound. Put foam or fiberglass inside the enclosure to soak up noise. Mount the generator on pads that stop shaking. Use silencers and special insulation to make it quieter. Plants or bushes between the generator and work areas help block sound. Make sure the ground is flat and the air can move around the generator.
Note: Let a pro install your generator. This helps you follow local rules and keeps things safe and quiet.
Think about both the first price and long-term costs. Diesel generators are cheaper to buy but cost more to run. They last longer and need less fixing. Natural gas generators cost more at first but save money on fuel. They can run longer without refueling. They need more care and cost more to keep up. Dual-fuel generators give you more options but are more complex. Rules for diesel can make things cost more. Always check fuel prices, care needs, and local laws before you choose.
Safety is very important. Check fuel lines and tanks often. Use transfer switches to keep the generator separate from the main power. Ground your generator the way the maker says. Point exhaust away from people. Hire a licensed electrician to put in and check your generator. Follow NFPA 110 rules for testing and care.
Safety Alert: Always use carbon monoxide alarms and keep your generator in a place with good airflow.
You have learned what a commercial generator does and how it works. You also know how to pick the right one for your business. Think about these things before you choose:
Pick standby or portable generator
Check what fuel you can use
Make sure it gives enough power
Look at where to put it and how loud it is
Think about how to keep it working and safe
Plan your budget and future costs
Getting the right size and using safety steps helps your business stay open when power goes out. Take time to look at what you need now and later. If you want gas generators or containerized sets, LIYU Group can help. Contact them to get more info or expert help for your business.
You should check your generator every month. Change the oil and filters after 100 hours of use. Test it weekly to make sure it starts. Always follow the manufacturer's guide for best results.
No, you should never run a generator indoors. It makes carbon monoxide, which is deadly. Always place it outside in a spot with good airflow. Use carbon monoxide alarms for extra safety.
Most small businesses need a generator between 20 kW and 100 kW. Make a list of your equipment. Add up the power needs. Always add extra capacity for safety.
A diesel generator can run for 24 to 72 hours if it has enough fuel. Natural gas units can run longer if the gas supply stays steady. Always check oil and coolant levels during long use.
Diesel and natural gas work best for most businesses. Diesel gives strong power and lasts long. Natural gas is cleaner and connects to pipelines. Pick the fuel that fits your needs and local rules.